-
×
 Zoom 400-Gallon RO Cartridge
15,0 ر.ع.
Zoom 400-Gallon RO Cartridge
15,0 ر.ع.
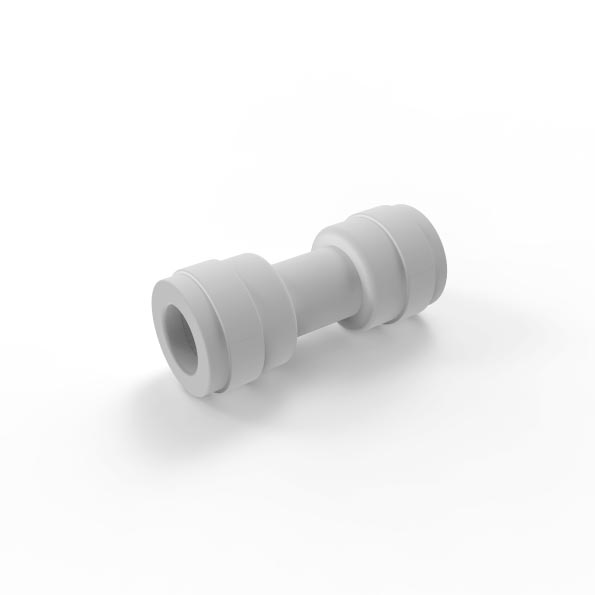
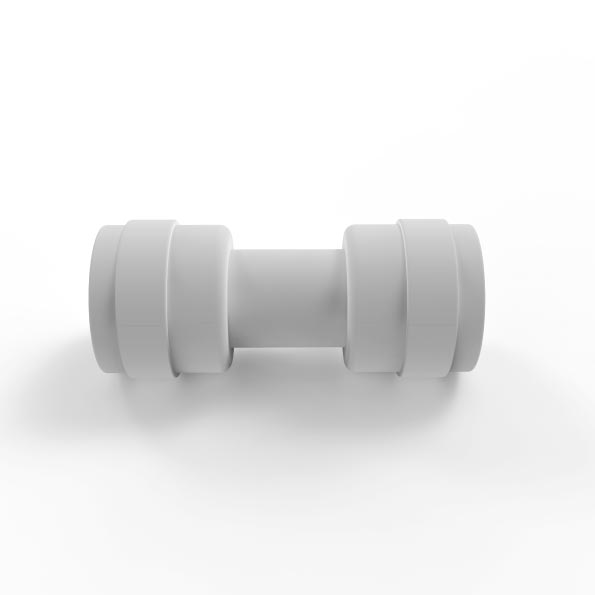
A Water Filter Tube Fitting Set (Class I) typically refers to a set of components designed for connecting water filtration system tubes or pipes. “Class I” may denote a standard or quality classification, ensuring the components meet certain specifications for durability, reliability, and safety.
These fittings are used to securely connect various parts of the water filtration system, such as filter cartridges, pipes, and water inlets/outlets. The fittings are usually made from durable materials such as plastic, brass, or stainless steel to prevent leaks and ensure long-term performance.
A typical Water Filter Tube Fitting Set could include various parts such as:
- Connectors: To join different sections of piping.
- Elbows: To change the direction of the tubing.
- Tees: To split water flow into multiple directions.
- Caps/Plugs: To seal unused ports.
These fittings are essential for the proper functioning of water filtration systems, allowing for easy installation, maintenance, and efficient water flow.

 العربية
العربية


















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.